The Illusion of Value
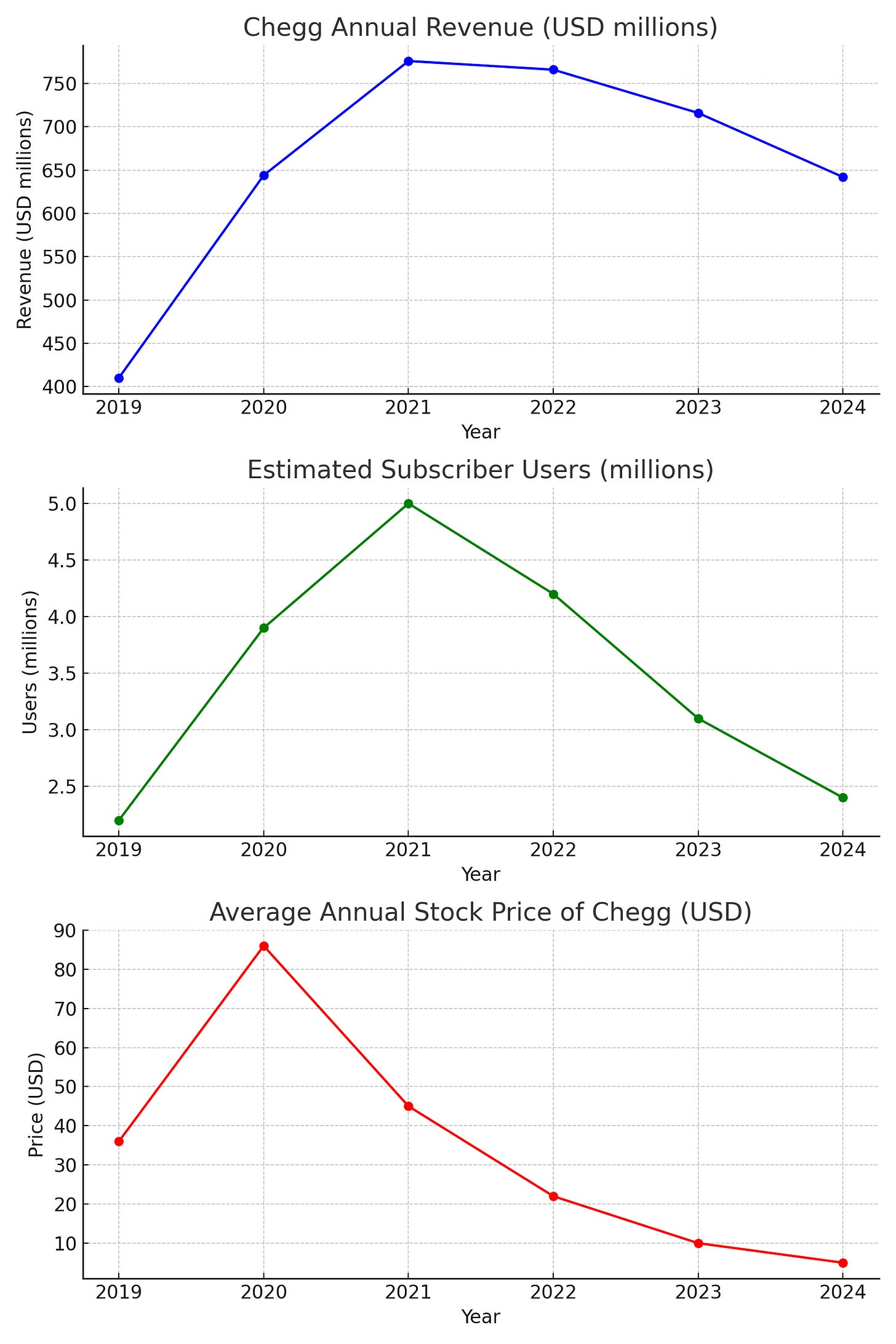
Chegg trades at extremely low multiples. At first glance, it looks like a bargain: it generates cash flow, remains profitable, and has no short-term liquidity issues. But beneath the surface, the business model is crumbling. The company is facing structural disruption, and its competitive advantages have likely vanished. The market is not being irrational — this may very well be a value trap.
The Legacy Business Is in Decline
For years, Chegg operated as an academic assistance platform: step-by-step solutions, homework help, exam prep, and so on. It was a success story during the digital education boom, especially during the pandemic.
Since 2022, however:
Active users and subscribers have steadily declined.
Revenue is in retreat.
Growth has vanished.
And this is not just a question of execution or timing. The problem is structural.
The AI Disruption
The arrival of tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or Khanmigo has changed the game:
Free or significantly cheaper.
More versatile than Chegg’s static offering.
Real-time, personalized responses with the ability to explain, summarize, and generate study materials.
Many students have abandoned Chegg for these new alternatives — and it’s easy to understand why.
CheggMate: Too Little, Too Late
In 2023, Chegg tried to jump on the AI wave with its own product: CheggMate, a GPT-4-based integration with its educational database.
The result has been underwhelming:
No return to growth.
No halt in user churn.
No clear competitive edge.
Worse still: it sends the message that Chegg no longer owns the tech — it's just another UI layer on top of a third-party model.
Valuation: Is It Really Cheap?
Metrics like a sub-5 P/E, low EV/EBITDA, or positive cash flow don’t tell the whole story. They reflect a business that used to work… but no longer does. If future earnings disappear, those “low” multiples will vanish too.
Low valuation does not equal undervaluation. Sometimes it simply reflects realistic — or pessimistic — expectations.
Value Trap Warning Signs
Structural revenue decline
No defensible moat vs. AI or free content
Reinvention attempts have failed
Significant convertible debt (~$1 billion)
Reputational issues (associated with academic cheating)
Conclusion
Chegg no longer has a sustainable competitive advantage. Its product has become irrelevant for many students, and its strategic response has fallen short. It may look cheap, but it’s not if the business continues to erode.
Not every cheap stock is undervalued. And not every low multiple signals opportunity. Chegg is a textbook example of how a once-profitable company can drift toward irrelevance if it fails to adapt.
More on how AI disruption is affecting Chegg here.